Improving access to clinical trials
Clinical trials are the single best way to turn advances in science into patient benefits. The ICR has a vision that a suitable trial should be made available for every person with cancer who wants to be part of one.

Expanding trial access – ICR report
Our 2021 report, Clinical trials in cancer, reveals the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on cancer trials and highlights longstanding barriers to expanding clinical trial access to more people with cancer. But Covid-19 also offers clues to a recovery that can get new treatments to cancer patients more quickly.
News: Cancer trial recruitment drops by 60 per cent during pandemic
The number of cancer patients entering clinical trials has plummeted during the pandemic – denying many thousands the latest treatment options and delaying drug development. Here, cancer experts set out their findings about the barriers to carrying out clinical trials in the UK and proposals for boosting participation.Latest ICR News
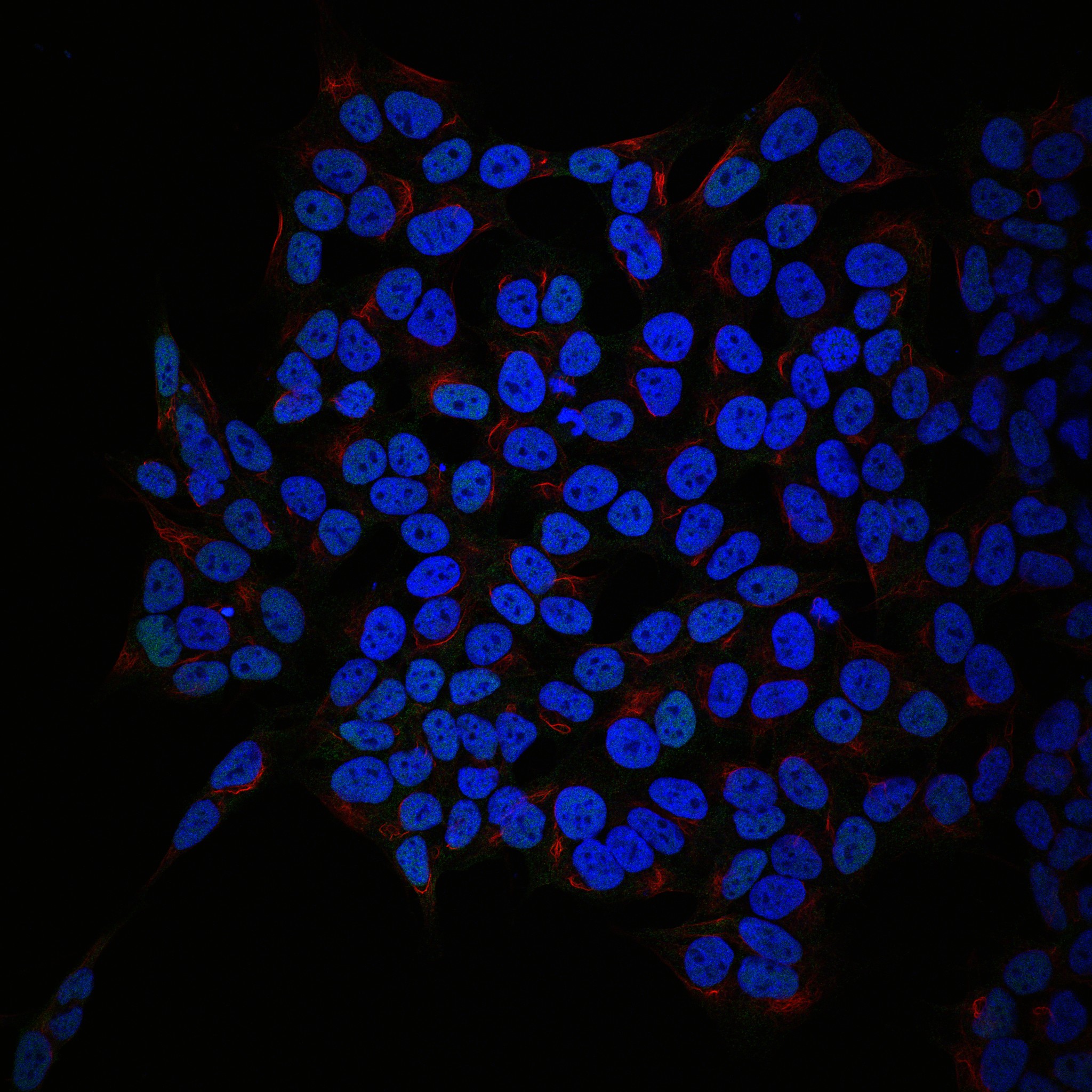
New research reveals how subtle genetic differences shape neuroblastoma behaviour
Researchers have shown that subtle mutational differences in a gene called ATRX help explain why children with the same type of neuroblastoma respond differently to treatment. These findings could support precise therapy recommendations based on a stronger understanding of the disease’s underlying biology.
New study shows promise for more reliable imaging of an important tumour characteristic
A team of scientists at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, has developed a repeatable three-dimensional (3D) imaging technique that could transform preclinical cancer studies.

ICR appoints global business leader as new Trustee
Dr Michelle Harrison – an international business leader with three decades of experience advising clients in global public policy, public affairs and brand building – has joined the Board of Trustees of The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
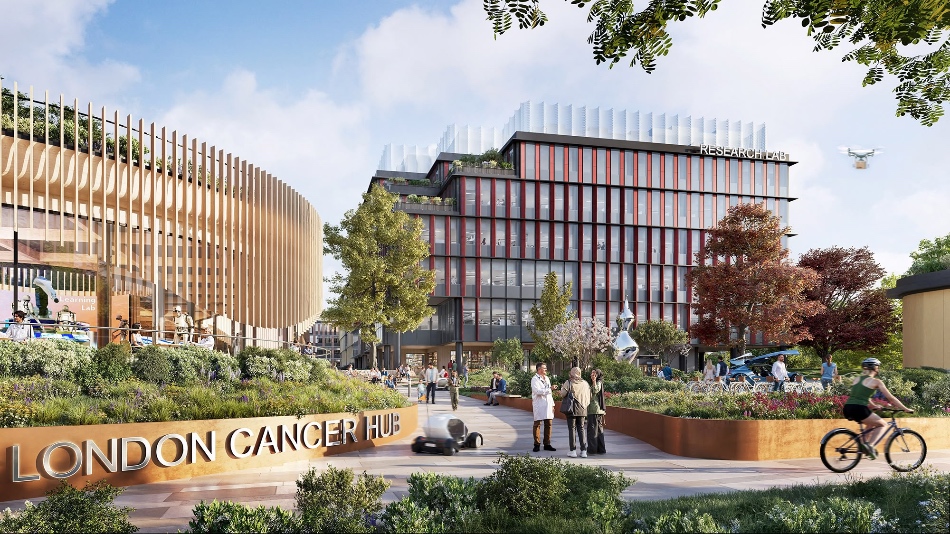

ICR welcomes approval of plans for major life-sciences district The London Cancer Hub
The Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) has welcomed the approval of ambitious new plans to create a home for oncology and life-sciences companies in Sutton, south London.